Before Start
- Make sure you have Hadoop installed. If you don’t have one, you can refer this link to install Hadoop.
- My current cluster consists of four VMs: master, slave1, slave2, slave3, slave4 on AWS and have installed fully distributed Hadoop-2.6.5 on them.
Necessary Tools and Dependencies
Maven
Download Maven from Maven Download Page.

I download maven to my directory, and using following command to extract it:
tar -xzvf apache-maven-3.5.3-bin.tar.gz
then, edit the ~/.bash_profile file:
vim ~/.bash_profile
add the following:
export M2_HOME=/home/ubuntu/apache-maven-3.5.3
export PATH=$PATH:$M2_HOME/bin
then source it to make it take effect:
source ~/.bash_profile
Then using the command to test whether you have successfully installed maven.
mvn -version
It should show the version information of the maven you have installed.

Install Mysql
First, install mysql server using the following command:
sudo apt-get install mysql-server
During the installation, it requires you to set password for root user, later you have to use this password to login Mysql.
Then using the following command to install mysql client:
sudo apt install mysql-client
And some dependencies are necessary for using mysql, use the following command to install them:
sudo apt install libmysqlclient-dev
Download Other Necessary Packages
The following packages are required, because of copyright reason, you can find your own way to download these packages online.
- ext-2.2.zip
- mysql-connector-java-8.0.11.jar
- doxia-module-twiki-1.0-alpha-9.2y.jar
- pentaho-aggdesigner-algorithm-5.1.5-jhyde.jar
- doxia-core-1.0-alpha-9.2y.jar
The first two packages are necessary for Oozie.
And the last three packages, I think is optional. But a lot of people recommended to put them in maven’s library, so I put them under the directory of apache-maven-3.5.3/lib/.
Download and Compile Oozie
Download Oozie from its offical website, I am using oozie-4.3.1.

then extract it:
tar -xzvf oozie-4.3.1.tar.gz
then, edit the pom.xml file:
vim pom.xml
Because my Hadoop version is 2.6.5, so I configured the following property to be 2.6.5. You have to change this value to be the corresponding Hadoop version in your cluster.

After editing this, using the following command to compile Oozie:
bin/mkdistro.sh -DskipTests -Puber
Then, if compile succeed, then you can find Oozie oozie-4.3.1-distro-tar.gz under the directory of distro/target. Copy this to the home directory, and rename the uncompiled Oozie:
mv oozie-4.3.1-distro-tar.gz ~
cd ~
mv oozie-4.3.1 oozie-4.3.1_
then unzip oozie-4.3.1-distro-tar.gz:
tar -xzvf oozie-4.3.1-distro.tar.gz
Change ~/.bash_profile
vim ~/.bash_profile
add the following into it:
export OOZIE_HOME=/home/ubuntu/oozie-4.3.1
export OOZIE_CONFIG=$OOZIE_HOME/conf
export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:$OOZIE_HOME/bin
then source it:
source ~/.bash_profile
Edit Hadoop core-site.xml
vim ~/hadoop-2.6.5/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
add the following into it:
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.ubuntu.hosts</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.ubuntu.groups</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>

Note that, the circled part in the above file is the current user of your computer, as shown in the following picture.

Change Oozie-site.xml in oozie
Firstly, enter Oozie configuration directory:
cd ~/oozie-4.3.1/conf
and edit oozie-site.xml, adding the following:
<property>
<name>oozie.service.JPAService.jdbc.driver</name>
<value>com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>oozie.service.JPAService.jdbc.url</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/oozie</value> </property>
<property>
<name>oozie.service.JPAService.jdbc.username</name>
<value>oozie</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>oozie.service.JPAService.jdbc.password</name>
<value>mysql</value>
</property>
<property> <!--change to your hadoop configuration directory--><name>oozie.service.HadoopAccessorService.hadoop.configurations</name>
<value>*=/home/ubuntu/hadoop-2.6.5/etc/hadoop</value>
</property>
<property> <!-- master is the host name for master -->
<name>oozie.service.WorkflowAppService.system.libpath</name>
<value>hdfs://master:9000/user/ubuntu/share/lib</value>
</property>
Note the following two things:
1. ubuntu in the following part is the same as the one in Hadoop’s core-site.xml. This path is the share library path of Oozie in HDFS.
 2. for the following properties, the first one is the username of mysql database user, and second one is its corresponding password. This should be the same as the user information you are about to create in Oozie.
2. for the following properties, the first one is the username of mysql database user, and second one is its corresponding password. This should be the same as the user information you are about to create in Oozie.

Create a Mysql User
Here I used oozie as username, and mysql as password. So I am going to create a Mysql user. Then enter mysql:
mysql -uroot -p
enter the password you set while you install mysql, then you should see the following:
 create an oozie database:
create an oozie database:
CREATE DATABASE oozie;
then create a mysql user:
CREATE USER 'oozie'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'mysql';
This command means: creating an user oozie, using mysql as its password. and allow this user to access mysql from any host.
Then we authorize user oozie the right to access database oozie:
GRANT ALL ON oozie.* TO 'oozie'@'%';
ALL stands for all right, the first oozie is the database name, * after the dot means all tables in this database. The second oozie stands for the user oozie. Finally, type the following command to make all previous authorization take effect:
FLUSH privileges;
then using the following command to exit mysql:
exit
Pack All Necessary jar Packages
First, enter oozie directory:
cd ~/oozie-4.3.1/
then, create a libext directory:
mkdir libext
Copy Hadoop jar packages to libext:
cp ../hadoop-2.6.5/share/hadoop/*/lib/*.jar libext/
cp ../hadoop-2.6.5/share/hadoop/*/*.jar libext/
Then also put the afore-downloaded two packages mysql-connector-java-8.0.11.jar and ext-2.2.zip to libext
cp ../mysql-connector-java-8.0.11.jar libext/
cp ../ext-2.2.zip libext/
Then we have to remove some packages that may create conflicts:
cd libext
mv servlet-api-2.5.jar servlet-api-2.5.jar.bak
mv jsp-api-2.1.jar jsp-api-2.1.jar.bak
mv jasper-compiler-5.5.23.jar jasper-compiler-5.5.23.jar.bak
mv jasper-runtime-5.5.23.jar jasper-runtime-5.5.23.jar.bak
mv slf4j-log4j12-1.7.5.jar slf4j-log4j12-1.7.5.jar.bak
then go back to oozie directory:
cd ~/oozie-4.3.1/
the next step is to pack oozie.war using the following command:
bin/oozie-setup.sh prepare-war
Edit Oozie-env.sh
Firstly, enter Oozie configuration directory:
cd ~/oozie-4.3.1/conf
and edit oozie-env.sh file:
# Set Java hoem and hadoop prefix
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
export OOZIE_PREFIX=/home/ubuntu/oozie-4.3.1
# Set hadoop configuration path
export OOZIE_CONF_DIR=/home/ubuntu/oozie-4.3.1/conf/
export OOZIE_HOME=/home/ubuntu/oozie-4.3.1
# add hadoop package
for file in $OOZIE_HOME/libext/*.jar
do
export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:$file
done
then, you have to source it to make it take effect:
source conf/oozie-env.sh
Upload Share Lib to HDFS
extract share lib in oozie directory:
tar -xzvf oozie-sharelib-4.3.1.tar.gz
then start hdfs deamon, yarn deamon and history server.
start-dfs.sh
start-yarn.sh
mr-jobhistory-deamon start historyserver
add share directory to the path you configured in oozie-site.xml:
bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user
bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/ubuntu
bin/hdfs dfs -put ../oozie-4.3.1/share /user/ubuntu/
Connect Oozie with Mysql
under oozie directory, using the following command to connect oozie with mysql:
bin/ooziedb.sh create -sqlfile oozie.sql -run
if this command throw “time zone unrecognized” error, using the following command:
mysql_tzinfo_to_sql /usr/share/zoneinfo/|mysql -u root mysql -p
enter your mysql password, and enter mysql:
mysql -u root -p
then set time zone to be UTC
set global time_zone="UTC";
flush privileges;
Start Oozie
Make sure you have already started hdfs deamon, yarn deamon and history server. Then in oozie directory, typing the following command to start oozie:
bin/oozied.sh start
You can use the following command to check the status of oozie:
bin/oozie admin --oozie http://localhost:11000/oozie -status
Run an Example
We are going to run the example provided by oozie. Firstly extract example in oozie directory:
tar -xzvf oozie-examples.tar.gz
configure the job.properties file in examples/apps/map-reduce:
vim examples/apps/map-reduce/job.properties
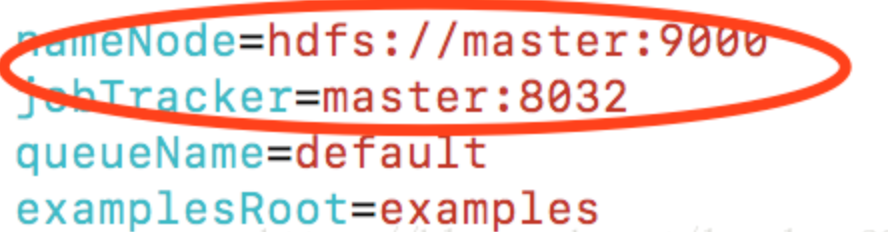 You have to change the configuration of
You have to change the configuration of nameNode and jobTracker. nameNode value is configured in Hadoop core-site.xml, and jobTracker value is configured in Hadoop yarn-site.xml under the property yarn.resourcemanager.address.
Then using the following command to upload this code to HDFS:
hdfs dfs -put ~/oozie-4.3.1/examples /user/ubuntu/
then, you can use the following command to execute this oozie job:
bin/oozie job -oozie http://localhost:11000/oozie -config examples/apps/map-reduce/job.properties -run
After submitting job, oozie will give you a job ID. You can use this Job ID to track your oozie job execution:
bin/oozie job -oozie http://localhost:11000/oozie -info 0000000-180614231856836-oozie-ubun-W
 After you see SUCCESS, you can print out the execution result using following command:
After you see SUCCESS, you can print out the execution result using following command:
hdfs dfs -cat /user/ubuntu/examples/output-data/map-reduce/part-00000

-
Previous
Hadoop Rack Awareness Configuration -
Next
Unikernels, Rise of the virtual library operating system